FC configuration and provisioning workflow
When you make storage available to a host using FC, you provision a volume and LUN on the storage virtual machine (SVM) , and then connect to the LUN from the host.
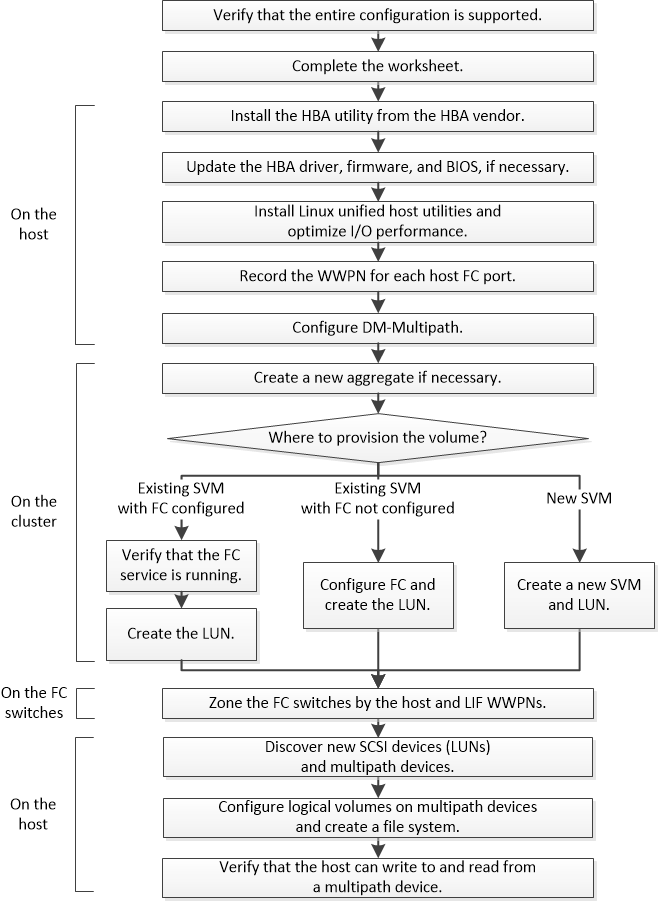
- Verifying that the FC configuration is supported
For reliable operation, you must verify that the entire FC configuration is supported. - Completing the FC configuration worksheet
You require FC initiator and target WWPNs and storage configuration information to perform FC configuration tasks. - Installing the HBA utility from the HBA vendor
The HBA utility enables you to view the worldwide port name (WWPN) of each FC port. The utility is also useful for troubleshooting FC issues. - Updating the HBA driver and firmware
If the FC host bus adapters (HBAs) in the Linux host are not running supported driver and firmware versions, you must update them. - Installing Linux Unified Host Utilities and optimizing I/O performance
Linux Unified Host Utilities software includes the sanlun utility, a Lenovo LUN reporting tool that you can use to display information about storage cluster nodes and Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) that are on the Linux host . You must also enable the correct server profile on the Linux host to optimize Lenovo storage performance. - Recording the WWPN for each host FC port
The worldwide port name (WWPN) is required to zone the FC switches and to create the igroups that allow the host to access its LUN. - Configuring DM-Multipath
DM-Multipath manages multiple paths between the Linux host and the storage cluster. Configuring DM-Multipath on a LUN, which appears to the Linux host as a SCSI device, enables your Linux host to access its LUN on the storage cluster if a path or component fails. - Creating an aggregate
If you do not want to use an existing aggregate, you can create a new aggregate to provide physical storage to the volume which you are provisioning. - Deciding where to provision the volume
Before you provision a volume to contain your LUNs, you need to decide whether to add the volume to an existing storage virtual machine (SVM) or to create a new SVM for the volume. You might also need to configure FC on an existing SVM . - Zoning the FC switches by the host and LIF WWPNs
Zoning the FC switches enables the hosts to connect to the storage and limits the number of paths. You zone the switches using the management interface of the switches. - Discovering new SCSI devices (LUNs) and multipath devices
LUNs on the storage cluster appear to the Linux host as SCSI devices, which are I/O paths that DM-Multipath aggregates into a new device, called a multipath device. The host does not automatically discover new SCSI devices (LUNs) that you add to your system. You must manually rescan them to discover them. - Configuring logical volumes on multipath devices and creating a file system
When the Linux host first accesses a new SCSI device (LUN), there is no partition or file system. If you want to use a partitioned multipath device, you must first partition the underlying SCSI devices. You might also want to create logical volumes on multipath devices, and optionally create a file system. - Verifying that the host can write to and read from a multipath device
Before using a multipath device, you should verify that the host can write data to the multipath device and read it back.
Give documentation feedback