Memory module configuration
Memory performance depends on several variables, such as memory mode, memory speed, memory ranks, memory population and processor.
Information about optimizing memory performance and configuring memory is available at the Lenovo Press website:
In addition, you can take advantage of a memory configurator, which is available at the following site:
Lenovo Enterprise Solutions Configurator (Memory Configurations)
Specific information about the required installation order of memory modules in your compute node based on the system configuration and memory mode that you are implementing is shown below.
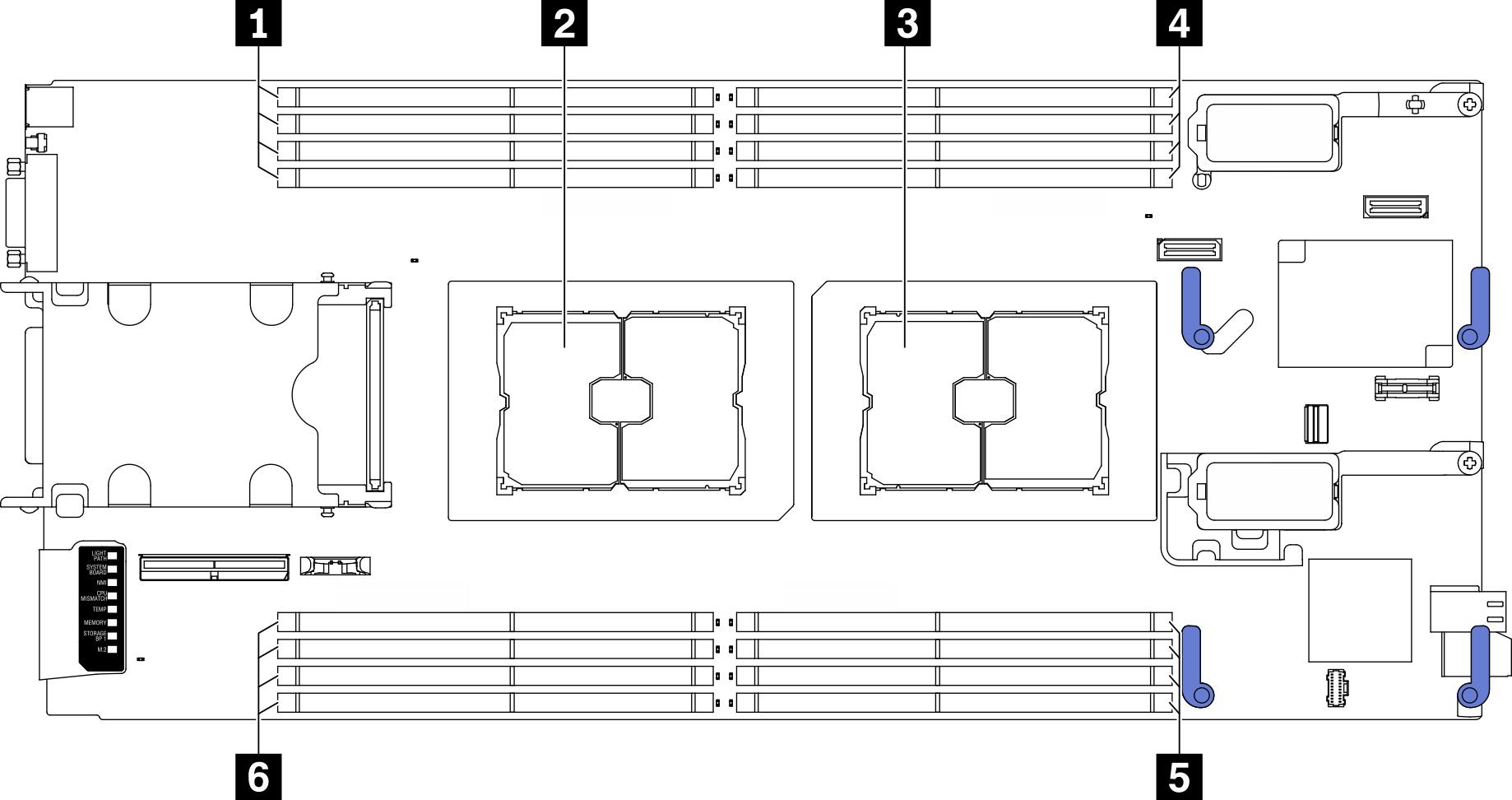
| 1 Memory module slot 9–12 | 4 Memory module slot 1–4 |
| 2 Processor socket 2 | 5 Memory module slot 5–8 |
| 3 Processor socket 1 | 6 Memory module slot 13–16 |
The memory-channel configuration table below shows the relationship between the processors, memory controllers, memory channels, and memory module slot numbers.
| Processor | Processor 1 | Processor 2 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel | B | A | D | C | G | H | E | F | F | E | H | G | C | D | A | B | |
| Memory module slot number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
Memory module installation guideline
- Two types of configurations are supported. Consider corresponding rules and population sequence accordingly:
DRAM memory module installation order (RDIMMs or 3DS RDIMMs)
A label on each DIMM identifies the DIMM type. This information is in the format xxxxx nRxxx PC4-xxxxx-xx-xx-xxx. Where n indicates if the DIMM is single-rank (n=1) or dual-rank (n=2).
At least one DIMM is required for each processor. Install at least eight DIMMs per processor for good performance.
When you replace a DIMM, the server provides automatic DIMM enablement capability without requiring you to use the Setup utility to enable the new DIMM manually.
Mixing x4 and x8 DIMMs in the same channel is allowed.
Install DIMMs of the same speed for optimal performance. Otherwise, the BIOS will find and run the lowest speed among all channels.