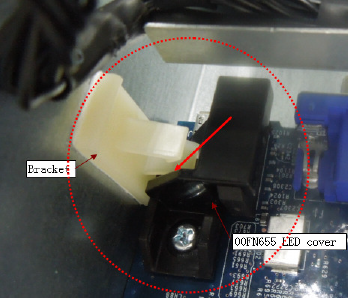
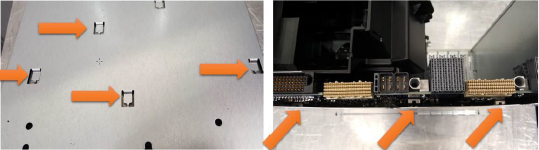
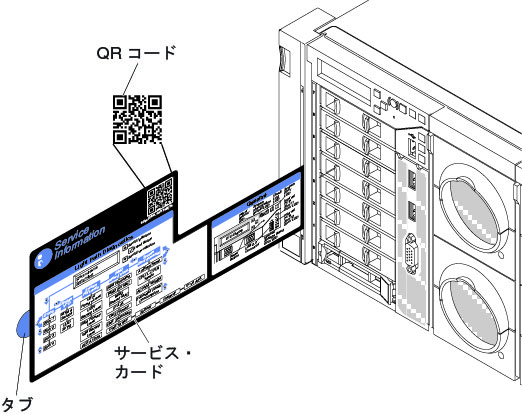
IBM to Lenovo server upgrade procedure
This topic describes how to perform the IBM to Lenovo (ITL) upgrade of an IBM System x3850 X6 and x3950 X6 Type 3837 server to a Lenovo System x3850 X6 and x3950 X6 Type 6241 server.
Installing an IBM to Lenovo (ITL) upgrade kit in an IBM System x3850 X6 and x3950 X6 Type 3837 server upgrades it to a Lenovo System x3850 X6 and x3950 X6 Type 6241 server, allowing the server to receive the latest system updates and improvements from Lenovo.
Upgrade task summary
Several processes need to be completed to perform an IBM to Lenovo server upgrade. Some tasks must be completed to prepare for the upgrade in advance of performing the actual upgrade. Each task is described in detail by the sub-topics following the task summary.
In advance of performing the ITL upgrade, the customer needs to complete the following tasks:
Order the ITL upgrade kit for the server.
Verify access to IBM websites.
Request transfer of Features on Demand (FoD) keys or new FoD keys.
When the service technician is ready to perform the ITL upgrade, they will need to complete the following tasks before they begin:
Download the latest versions of IBM and Lenovo software tools needed to perform the ITL upgrade.
Make sure that the FoD key transfer was completed or that new FoD keys were received.
Verify the contents of the ITL upgrade kit.
Record the system information needed to upgrade the Lenovo service agreements.
Backup the IBM server configuration and vital product data (VPD).
To perform the ITL upgrade, service technician will complete the following tasks:
Replace IBM components with the Lenovo components included in the ITL upgrade kit.
Update server firmware to the latest Lenovo version.
Restore the server configuration and VPD.
Restore the transferred FoD keys or install the new FoD keys.
Relabel the server as a Lenovo server.
After the ITL upgrade is complete, the service technician will verify that the conversion is successful and update the customer records.
Preparing for the upgrade
Before a a service technician can begin upgrading a customer server, the customer must complete the following tasks, in advance:
Order the correct ITL kit for the Lenovo x3850 X6 or Lenovo x3950 X6 server.
Verify that the customer IDs and passwords are valid for the IBM Support portal (http://www.ibm.com/support/), IBM Fix Central (http://www.ibm.com/support/fixcentral/), and the Features on Demand (FoD) website (https://fod.lenovo.com/lkms). The customer will need to access these IBM websites to download tools and information for their IBM server before the service technician can perform the upgrade.
If any Features on Demand (FoD) options or features are being used in the IBM server, the customer must complete the following steps to manually transfer or request new FoD keys for use in the Lenovo server:
Make a list of all the FoD activation keys that are active for the IBM server. Select Retrieve history at the Features on Demand website (https://www.ibm.com/systems/x/fod) to view the active keys for the IBM server.
Verify which FoD are installed in the IBM server (see the IBM Integrated Management Module II User's Guide at https://www.ibm.com/support/entry/portal/docdisplay?lndocid=MIGR-5086346 for information about how to check if FoD keys are installed in the server and instructions about how to import and export the FoD keys).
Request a manual transfer of the FoD activation keys from the original IBM machine type to the new Lenovo machine type, or request new FoD activation keys for use with the new Lenovo machine type. To request a manual transfer or new activation keys, the customer must send an email request to Features on Demand Support at fod@lenovo.com. Make sure that this email includes a reference to the ITL kit and provides the following information:
The original IBM server serial number.
The machine type of the original IBM server (Type 3837).
The machine type of the upgraded Lenovo server (Type 6241).
A list of the FoD activation keys to transfer or replace, that were gathered in step 3a.
Before you begin
Before the service technician can begin physically upgrading the server, the customer and service technician must complete the following tasks:
Download the following software tools and associated documentation. Both IBM and Lenovo tools are needed to backup and restore the server configuration. IBM tools will be used to backup server configuration information in preparation for the ITL upgrade. Lenovo tools will be used to restore server configuration information after the ITL upgrade.
IBM Advanced Settings Utility (https://www.ibm.com/support/entry/portal/docdisplay?lndocid=tool-asu)
Lenovo Advanced Settings Utility (the Advanced Settings Utility (ASU) for Lenovo x86 servers website)
Lenovo Bootable Media Creator (the Bootable Media Creator (BoMC) for Lenovo x86 servers website)
Lenovo UpdateXpress (the UpdateXpress website)
Verify that the IBM Features on Demand activation keys that were previously requested for transfer or replacement are available to install on the upgraded Lenovo server.
Verify the contents of the ITL upgrade kit:
The Lenovo x3850 X6 ITL upgrade kit contains:
One standard I/O book
One 4U-high right EIA bezel with Lenovo logo
One service card
System information update labels
One MAC address label
The Lenovo x3950 X6 ITL upgrade kit contains:
Two standard I/O books
One 8U-high right EIA bezel with Lenovo logo
One service card
System information update labels
Two MAC address labels
Record (take a photograph of the barcode label or write down the barcode number) the 11S serial number for each Lenovo standard I/O book that comes with the ITL kit. This is required to update the customer entitlement and service offering support.
NoteYou will need the server IMM IP address, user name, and password to perform the following step. If you are upgrading a x3950 server, you will need the IP address for both IMMs.Using the IBM Advanced Settings Utility (ASU) tool, backup (export) the system configuration, Features on Demand (FoD) keys, and vital product data (VPD) for the IBM server.
NoteSee theIBM Integrated Management Module II User's Guide at https://www.ibm.com/support/entry/portal/docdisplay?lndocid=MIGR-5086346 and the IBM Advanced Settings Utility User's Guide at http://toolscenter.lenovofiles.com/help/topic/asu/asu_guide.pdf for information about how to use these tools and commands. Access the IBM ASU tool
Access the IBM ASU tool by completing the following steps:
NoteFor an IBM System x3950 X6 8-socket system, the following procedure must be performed twice, once for each of thestandard I/O books in the system. Connect a laptop computer to the IMM management network port of the server.
Configure your laptop operating system network settings to match the IMM network settings.
Open a command prompt and navigate to the directory where the ASU files are installed.
NoteTo run the ASU commands, you must be in the directory where the ASU files are installed.Backup system configuration
To backup the system configuration of the IBM server to a file, use the ASU save <filename> command, where <filename> is the complete path name of the file where the configuration is to be saved.
Backup Features on Demand (FoD) keys
To backup the Features on Demand (FoD) keys of the IBM server:To export the FoD inventory information for the IBM server, use the ASU fodcfg reportkey command.
To export the FoD keys for the IBM server, use the ASU fodcfg exportkey command.
Backup vital product data (VPD)
NoteMake sure that you are using the latest version of the IBM ASU tool.
For an IBM System x3950 X6 8-socket system, the following procedure must be performed twice, once for each of the standard I/O books in the system.
To backup the VPD data for the IBM server:
To save the VPD information for an IBM System x3850 X6 4–socket system, complete the following steps. Save the files in secure location, as the values they contain will need to be re-entered after installing the new Lenovo standard I/O book.
To save the system VPD information into a file, run the ASU command:
asu64 show SYSTEM_PROD_DATA --host <IMM IP> --user <IMM userid> --password <IMM password> > <serial>_system.txt
where:
- <IMM IP> is the IMM IP address
- <IMM userid> is the IMM user name
- <IMM password> is the IMM password
- <serial> is the serial number of the standard I/O book (allows each data file to be identified)
To save the system component VPD information into a file, run the ASU command:
asu64 show VPD --host <IMM IP> --user <IMM userid> --password <IMM password> > <serial>_component.txt
where:
- <IMM IP> is the IMM IP address
- <IMM userid> is the IMM user name
- <IMM password> is the IMM password
- <serial> is the serial number of the standard I/O book (allows each data file to be identified)
To save the VPD information for an IBM System x3950 X6 8–socket system, complete the following procedures. Save the files in secure location, as the values they contain will need to be re-entered after installing the new Lenovo standard I/O books.
To save the system VPD information for node 1 of an IBM System x3950 X6 8–socket system, complete the following steps:
To save the system VPD information for node 1 into a file, run the ASU command:
asu64 show SYSTEM_PROD_DATA --host <IMM IP> --user <IMM userid> --password <IMM password> > <serial>_Node1_system.txt
where:
- <IMM IP> is the IMM IP address
- <IMM userid> is the IMM user name
- <IMM password> is the IMM password
- <serial> is the serial number of the standard I/O book (allows each data file to be identified)
To save the system component VPD information for node 1 into a file, run the ASU command:
asu64 show VPD --host <IMM IP> --user <IMM userid> --password <IMM password> > <serial>_Node1_component.txt
where:
- <IMM IP> is the IMM IP address
- <IMM userid> is the IMM user name
- <IMM password> is the IMM password
- <serial> is the serial number of the standard I/O book (allows each data file to be identified)
To save the system VPD information for node 2 of an IBM System x3950 X6 8–socket system, complete the following steps:
To save the system VPD information for node 2 into a file, run the ASU command:
asu64 show SYSTEM_PROD_DATA --host <IMM IP> --user <IMM userid> --password <IMM password> > <serial>_Node2_system.txt
where:
- <IMM IP> is the IMM IP address
- <IMM userid> is the IMM user name
- <IMM password> is the IMM password
- <serial> is the serial number of the standard I/O book (allows each data file to be identified)
To save the system component VPD information for node 2 into a file, run the ASU command:
asu64 show VPD --host <IMM IP> --user <IMM userid> --password <IMM password> > <serial>_Node2_component.txt
where:
- <IMM IP> is the IMM IP address
- <IMM userid> is the IMM user name
- <IMM password> is the IMM password
- <serial> is the serial number of the standard I/O book (allows each data file to be identified)
Make sure that the server is operating correctly and that there are no errors messages (see Error messages). Correct any problems that are indicated, unless they relate to components or firmware being replaced as part of the ITL upgrade.
Perform the ITL upgrade
To upgrade an IBM server to a Lenovo server, the service technician must complete the following steps:
Update firmware and device drivers for installed components
After performing the physical conversion and updating server firmware, the service technician must also update the firmware and device drivers for all components installed in the server to their Lenovo versions. Lenovo firmware and device drivers for installed components are available at the Lenovo Data Center Support website. See the documentation for each device for additional information about how to perform the update.
Verification
After the ITL server upgrade is complete, the service technician must complete the following steps to verify operation of the Lenovo server:
Make sure that the server powers up and passes UEFI initialization (see Turning on the server and Using the Setup utility).
Make sure that you are able to access the IMM (see Using the integrated management module).
Verify that all server vital product data (VPD) is correct (see the Integrated Management Module II User’s Guide at the Integrated Management Module II User’s Guide ).
Make sure that all server firmware is updated to the latest level (see Updating the firmware).
Make sure that there are no errors messages (see Error messages).
If problems are encountered following the ITL upgrade, troubleshoot the system using standard methods (see Start here). If you are unable to resolve the problem, open an online service request, go to the Service requests and PMRs website. Be prepared to provide information about any error codes and collected data.
Update customer and service records
After the ITL server upgrade is complete and verified, the service technician must contact regional support to update customer and service records as soon as possible after completing the ITL upgrade. Refer to “Servicer Only Tech Tip Document ID 5097919” for detailed contact information.
The following information is required to update the customer entitlement database:
The original IBM server Machine Type and serial number.
The upgraded Lenovo server Machine Type and serial number.
Include a photograph of the 11S barcode or type the serial number for each Lenovo standard I/O book that was installed.
IBM parts are property of the customer and should be left with the customer.
Service technicians in each geography should report the upgrade activity, as follows:
For USA and China, record SC 44, AC01 against the original IBM Machine Type and serial number.
For EMEA, record SC 46, AC06 against the RCMS case opened for the original IBM Machine Type and serial number.
For Canada, record SC 33, ECA=DRA against the original IBM Machine Type and serial number.
| Region | Contact | |
|---|---|---|
| NA | DCG_SERVICE@lenovo.com | |
| EMEA | Note Make sure that you copy Mark Hof (mhof@lenovo.com) on all EMEA inquires | |
| UKIR | Steven Anderson3 (sanderson3@lenovo.com) | |
| France/Benelux/Scandin. & Finland | Regis Clermont (rclermont@lenovo.com) | |
| Italy/Iberia | Samuel Benedetti (sbenedetti@lenovo.com) | |
| North-West Africa | Angel Carreras Fernandez1 (afernandez1@lenovo.com) | |
| Russia/EECA | Alexander Totikov (atotikov@lenovo.com) | |
| PL, CZ and SK (AR+UN)/ SEE (IN+UN)/ Greece (IN+UN | Mark Hof (mhof@lenovo.com) Acting | |
| Middle-East/Pakistan | Alaa Halime (ahalime@lenovo.com) | |
| DACH (Shared)/Israel (Andre)/ Baltics (Andre) | Uwe Nunweiler (ununweiler@lenovo.com) | |
| Southern Africa/Eastern Africa/Egypt and Turkey | Amir Yassien (ayassien@lenovo.com) | |
| AP/PRC | Kevin Yuan (yuanxh2@lenovo.com) | |