Shelf-to-shelf connection rules
When you have more than one disk shelf in a stack of disk shelves, they connect to each other through each SAS domain (IOM A and IOM B) using the applicable standard
or double-wide
shelf-to-shelf cabling. Your use of standard
or double-wide
shelf-to-shelf cabling depends on the configuration you have.
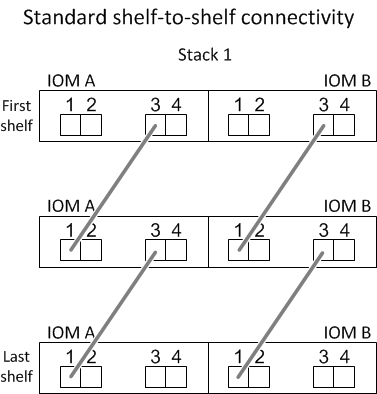
Standard shelf-to-shelf connectivity
- Standard shelf-to-shelf connectivity is used in multipath HA, multipath, single-path HA, and single-path configurations.
- Standard shelf-to-shelf connectivity is what is being used in existing SAS storage configurations with IOM3 and IOM6 modules: one cable connection is needed between isk shelves in each domain—domain A (IOM A) and domain B (IOM B).
- Best practice is to use IOM ports 3 and 1 for standard shelf-to-shelf connectivity.
From the logical first shelf to the logical last shelf in a stack, you connect IOM port 3 to the next shelf's IOM port 1 in domain A and then domain B.
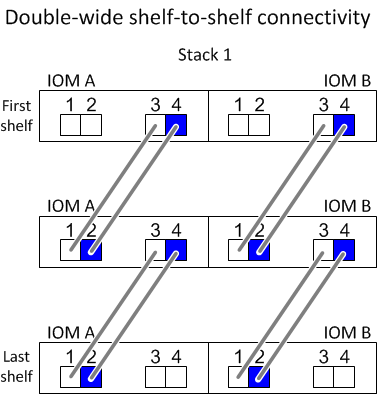
Double-wide shelf-to-shelf connectivity
- Double-wide shelf-to-shelf connectivity is used in quad-pathed (quad-path HA and quad-path) configurations.
- Double-wide shelf-to-shelf connectivity requires two cable connections between disk shelves in each domain—domain A (IOM A) and domain B (IOM B).
The first cable connection is cabled as standard shelf-to-shelf connectivity (using IOM ports 3 and 1); the second cable connection is cabled as double-wide shelf-to-shelf connectivity (using IOM ports 4 and 2).
From the logical first shelf to the logical last shelf in a stack, you connect IOM port 3 to the next shelf's IOM port 1 in domain A and then domain B. From the logical first shelf to the logical last shelf in a stack, you connect IOM port 4 to the next shelf's IOM port 2 in domain A and then domain B. (IOM ports cabled as double-wide connectivity are shown with blue.)