Hot-removing disk shelves with IOM12 modules
You can hot-remove a disk shelf with IOM12 modules—nondisruptively remove a disk shelf from a system that is powered on and serving data (I/O is in progress)—when you need to move or replace the disk shelf. You can hot-remove one or more disk shelves from anywhere within a stack of disk shelves or remove a stack of disk shelves.
Before you begin
Your system must be a multipath HA, multipath, quad-path HA, or quad-path configuration.
For DM3000x, DM5000x, or DM7000x, the external storage must be cabled as multipath HA or multipath.NoteFor aDM3000x, DM5000x, or DM7000x single-controller system that has the external storage cabled with multipath connectivity, the system is a mixed-path configuration because the internal storage uses single-path connectivity. - HA pair configurations cannot be in a takeover state.
- You must have removed all aggregates from the disk drives—the disk drives must be spares— in the disk shelves you are removing.AttentionIf you attempt this procedure with aggregates on the disk shelf you are removing, you could fail the system with a multidisk panic.NoteBefore you remove all aggregates, identify the SVMs of the aggregates and remove all port sets, ports, LUNs, and volumes allocated to the SVMs. Then, remove the SVMs.
You can use the storage aggregate offline -aggregate aggregate_name command.
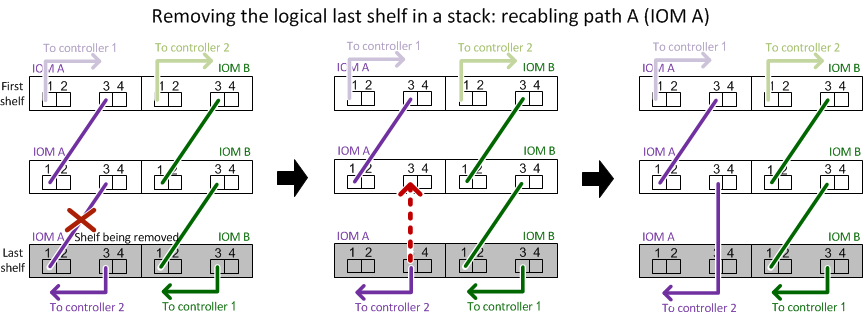
- If you are removing one or more disk shelves from within a stack, you must have factored the distance to bypass the disk shelves you are removing; therefore, if the current cables are not long enough, you need to have longer cables available.
About this task
Best practice is to remove disk drive ownership after you remove the aggregates from the disk drives in the disk shelves you are removing.
Removing ownership information from a spare disk drive allows the disk drive to be properly integrated into another node (as needed).
The procedure for removing ownership from a disk can be found in the Disks and Aggregates Power Guide.NoteThe procedure for removing ownership from disk drives requires you to disable disk ownership automatic assignment. You reenable disk ownership automatic assignment at the end of this procedure.- For a clustered ONTAP system that is greater than two-nodes, best practice is to have reassigned epsilon to an HA pair other than the one that is undergoing planned maintenance.
Reassigning epsilon minimizes the risk of unforeseen errors impacting all nodes in a clustered ONTAP system. Information about the role of quorum and epsilon, and the procedure for reassigning epsilon to another node in a cluster can be found in the System Administration Reference.
Find a System Administration Guide for your version of ONTAP 9
- If you are hot-removing a disk shelf from a stack (but keeping the stack), you recable and verify one path at a time (path A then path B) to bypass the disk shelf you are removing so that you always maintain single-path connectivity from the controllers to the stack.AttentionIf you do not maintain single-path connectivity from the controllers to the stack when recabling the stack to bypass the disk shelf you are removing, you could fail the system with a multidisk panic.