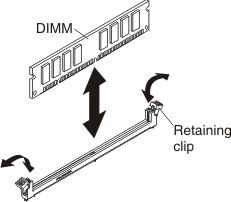
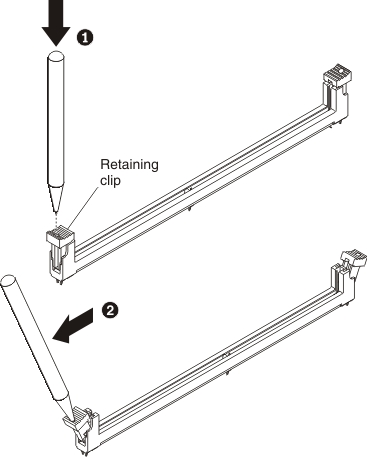
Installing a DIMM
Use this information to install a DIMM.
- Read Safety and Installation guidelines.
- Read the documentation that comes with the DIMMs.
- If the compute node is installed in a chassis, remove it (see Removing a compute node from a chassis for instructions).
- Carefully lay the compute node on a flat, static-protective surface, orienting the compute node with the bezel pointing toward you.
This component can be installed as an optional device or as a CRU. The installation procedure is the same for the optional device and the CRU.
After you install or remove a DIMM, you must change and save the new configuration information by using the Setup utility. When you turn on the compute node, a message indicates that the memory configuration has changed. Start the Setup utility and select Save Settings (see Using the Setup utility for more information) to save changes.
- Verify that the amount of installed memory is the expected amount of memory through the operating system, by watching the monitor as the compute node starts, by using the CMM sol command, or through Flex System Manager management software (if installed).
- For more information about the CMM sol command, see "Flex System Chassis Management Module: Command-Line Interface Reference Guide".
- For more information about Flex System Manager management software, see Flex System Manager documentation.
- Run the Setup utility to reenable the DIMMs (see Using the Setup utility for more information).
The compute node has a total of 24 dual inline memory module (DIMM) connectors. The compute node supports low-profile (LP) DDR4 DIMMs with error-correcting code (ECC) in 4 GB, 8 GB, 16 GB, 32 GB and 64 GB capacity.
The following illustration shows the system-board components, including DIMM connectors.
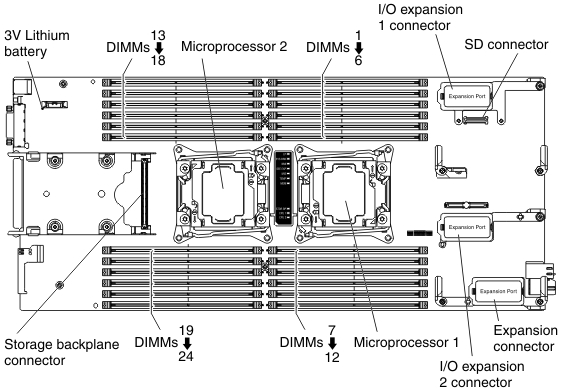
The memory is accessed internally through four channels. Each memory channel has three DIMM connectors for each microprocessor (six total). Each channel can have a maximum of eight ranks. The following table lists the memory channels and shows which DIMM connectors are in the channel for each microprocessor.
| Microprocessor | Memory channel | DIMM connectors |
|---|---|---|
| Microprocessor 1 | Channel A | 4, 5, and 6 |
| Channel B | 1, 2, and 3 | |
| Channel C | 7, 8, and 9 | |
| Channel D | 10, 11, and 12 | |
| Microprocessor 2 | Channel A | 19, 20, and 21 |
| Channel B | 22, 23, and 24 | |
| Channel C | 16, 17, and 18 | |
| Channel D | 13, 14, and 15 |
Depending on the memory mode that is set in the Setup utility, the compute node can support a minimum of 4 GB and a maximum of 768 GB of system memory in a compute node with one microprocessor. If two microprocessors are installed, the compute node can support a minimum of 8 GB and a maximum of 1536 GB of system memory.
Depending on the memory mode that is set in the Setup utility, the compute node can support a minimum of 4 GB and a maximum of 384 GB of system memory in a compute node with one microprocessor. If two microprocessors are installed, the compute node can support a minimum of 8 GB and a maximum of 768 GB of system memory.
The following notes describe information that you must consider when you install memory:
- Use only registered (RDIMM) DDR4 DIMMs.
- Maximum DIMM capacity:
- Registered DIMMs (RDIMMs): 768 GB (using 32 GB RDIMMs)
- Load Reduced DIMMs (LRDIMMs): 1536 GB (using 64 GB LRDIMMs)
- RDIMM sizes supported (GB): 4, 8, 16, 32
- LRDIMM sizes supported (GB): 32, 64
- You cannot mix RDIMMs and LRDIMMs in the same compute node.
- DIMMs are verified as authentic Lenovo modules by the UEFI software. If any non-authentic DIMMs are detected, an informational message appears in the system event log and memory performance might be limited. Non-authentic DIMMs are not covered by your Lenovo warranty.
- Install DIMMs in sets of four to optimize performance.
- Installing an equal amount of memory for each microprocessor is recommended.
- If DIMMs of different speeds are installed, memory on a channel operates at the speed of the lowest-speed DIMM in the channel.
- A total of eight ranks on each channel is supported.
- If multi-rank DIMMs are installed, install higher ranking DIMMS first starting in the connector at the end of the memory channel.
- Quad-rank RDIMMs are not supported.
- Rank multiplication is supported allowing up to three DIMMs per channel.
- If you install LRDIMMs in a 3 DIMM per channel configuration, performance might be reduced compared to standard DIMMs.
- Mixing of mirrored and non-mirrored modes is not supported.
- Lock-step channel mode is not supported.
The compute node supports the following DIMM speeds based on the number of DIMMs installed per channel:
| Memory Description | DIMMs per channel | Speed (MHz) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 GB (1Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 1 | 2133 MHz |
| 4 GB (1Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 2 | 2133 MHz |
| 4 GB (1Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 3 | 1600 MHz |
| 8 GB (1Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 1 | 2133 MHz |
| 8 GB (1Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 2 | 2133 MHz |
| 8 GB (1Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 3 | 1600 MHz |
| 8 GB (2Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 1 | 2133 MHz |
| 8 GB (2Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 2 | 2133 MHz |
| 8 GB (2Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 3 | 1600 MHz |
| 16 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 1 | 2133 MHz |
| 16 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 2 | 2133 MHz |
| 16 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 3 | 1866 MHz |
| 32 GB (2Rx4, 8 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 1 | 2133 MHz |
| 32 GB (2Rx4, 8 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 2 | 2133 MHz |
| 32 GB (2Rx4, 8 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz RDIMM | 3 | 1600 MHz / 1866 MHz |
| 32 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz LRDIMM | 1 | 2133 MHz |
| 32 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz LRDIMM | 2 | 2133 MHz |
| 32 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz LRDIMM | 3 | 1866 MHz |
| 64 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz LRDIMM | 1 | 2133 MHz |
| 64 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz LRDIMM | 2 | 2133 MHz |
| 64 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-17000 TruDDR4 2133 MHz LRDIMM | 3 | 1600 MHz / 1866 MHz |
| Memory Description | DIMMs per channel | Speed (MHz) |
|---|---|---|
| 8 GB (1Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 1 | 2400 MHz |
| 8 GB (1Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 2 | 2400 MHz |
| 8 GB (1Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 3 | 1866 MHz |
| 8 GB (2Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 1 | 2400 MHz |
| 8 GB (2Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 2 | 2133 MHz |
| 8 GB (2Rx8, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 3 | 1866 MHz |
| 16 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 1 | 2400 MHz |
| 16 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 2 | 2400 MHz |
| 16 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 3 | 1866 MHz |
| 32 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 1 | 2400 MHz |
| 32 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 2 | 2400 MHz |
| 32 GB (2Rx4, 4 Gbit, 1.2V) PC4-19200 DDR4 2400 MHz LP RDIMM | 3 | 1866 MHz |
- Independent-channel mode: Independent-channel mode provides a maximum of 768 GB of usable memory with one installed microprocessor, and 1536 GB of usable memory with two installed microprocessors (using 64 GB DIMMs).
- Independent-channel mode: Independent-channel mode provides a maximum of 384 GB of usable memory with one installed microprocessor, and 768 GB of usable memory with two installed microprocessors (using 32 GB DIMMs).
Rank-sparing mode: In rank-sparing mode, one memory DIMM rank serves as a spare of the other ranks on the same channel. The spare rank is held in reserve and is not used as active memory. The spare rank must have identical or larger memory capacity than all the other active DIMM ranks on the same channel. After an error threshold is surpassed, the contents of that rank is copied to the spare rank. The failed rank of DIMMs is taken offline, and the spare rank is put online and used as active memory in place of the failed rank.
The memory rank sparing mode requires an even number of DIMMs. If your server has an odd number of DIMMs installed, ensure that you disable the memory rank sparing mode from the Memory menu in Setup Utility. See Using the Setup utility.
NoteAfter disabling the memory rank sparing mode, if a message prompts that the memory configuration is not valid, restart the IMM2. Alternatively, you can turn off the server, disconnect it from and then reconnect it to ac power, and then turn on the server again.The following notes describe additional information that you must consider when you select rank-sparing memory mode:- Rank-sparing on one channel is independent of the sparing on all other channels.
- To use rank sparing, install at least one DIMM pair for each microprocessor. If a channel has only one DIMM and it is single-rank or dual-rank, do not attempt to use memory sparing.
- The effective memory that is available to the system is less than what is installed.
- You can use the Setup utility to determine the status of the DIMM ranks.
- Mirrored-channel mode: In mirrored-channel mode, memory is installed in pairs. Each DIMM in a pair must be identical in size and architecture. The channels are grouped in pairs with each channel receiving the same data. One channel is used as a backup of the other, which provides redundancy. The memory contents on channel A are duplicated in channel B, and the memory contents of channel C are duplicated in channel D. The effective memory that is available to the system is only half of what is installed.
One DIMM for each microprocessor is the minimum requirement. However, for optimal performance, install DIMMs in sets of four so that you distribute memory equally across all four channels. If two microprocessors are installed, distribute memory across all channels and equally between the microprocessors.
| Number of installed DIMMs | 1 microprocessor installed | 2 microprocessors installed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIMM slot number | DIMMs per channel | DIMM slot number | DIMMs per channel | |
| 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 2 | 9 | 16 | ||
| 3 | 1 | 9 | ||
| 4 | 12 | 21 | ||
| 5 | 5 | 2 | 1 | |
| 6 | 8 | 13 | ||
| 7 | 2 | 12 | ||
| 8 | 11 | 24 | ||
| 9 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 2 |
| 10 | 7 | 17 | ||
| 11 | 3 | 8 | ||
| 12 | 10 | 20 | ||
| 13 | Not used - maximum of 12 DIMMs in systems with 1 microprocessor | 2 | ||
| 14 | 14 | |||
| 15 | 11 | |||
| 16 | 23 | |||
| 17 | 6 | 3 | ||
| 18 | 18 | |||
| 19 | 7 | |||
| 20 | 19 | |||
| 21 | 3 | |||
| 22 | 15 | |||
| 23 | 10 | |||
| 24 | 22 | |||
| DIMM pair installation order | 2 DIMMs per channel | 3 DIMMs per channel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 microprocessor installed | 2 microprocessors installed | 1 microprocessor installed | 2 microprocessors installed | |
| 1 | 4 and 5 | 4 and 5 | 4, 5, and 6 | 4, 5, and 6 |
| 2 | 8 and 9 | 20 and 21 | 7, 8, and 9 | 19, 20, and 21 |
| 3 | 1 and 2 | 8 and 9 | 1, 2, and 3 | 7, 8, and 9 |
| 4 | 11 and 12 | 16 and 17 | 10, 11, and 12 | 16, 17 and 18 |
| 5 | n/a | 1 and 2 | n/a | 1, 2, and 3 |
| 6 | 23 and 24 | 22, 23, and 24 | ||
| 7 | 11 and 12 | 10, 11, and 12 | ||
| 8 | 13 and 14 | 13, 14, and 15 | ||
Install DIMMs in order as indicated in the following table for mirrored-channel mode.
| DIMM pair | 1 microprocessor installed | 2 microprocessors installed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIMM slot numbers | DIMMs per channel | DIMM slot numbers | DIMMs per channel | |
| 1 | 4 and 11 | 1 | 4 and 11 | 1 |
| 2 | 9 and 121 | 21 and 241 | ||
| 3 | 2 and 51 | 2 | 9 and 121 | |
| 4 | 8 and 111 | 13 and 161 | ||
| 5 | 3 and 61 | 3 | 2 and 51 | 2 |
| 6 | 7 and 101 | 20 and 231 | ||
| 7 | none | 8 and 111 | ||
| 8 | none | 14 and 171 | ||
| 9 | none | 3 and 61 | 3 | |
| 10 | none | 19 and 221 | ||
| 11 | none | 7 and 101 | ||
| 12 | none | 15 and 181 | ||
| ||||
To install a DIMM, complete the following steps:
- Install the cover onto the compute node (see Installing the compute node cover for instructions).
- Install the compute node into the chassis (see Installing a compute node in a chassis for instructions).