Power supplies
The Flex System Carrier-Grade chassis supports up to six autoranging power supplies.
The types of power supplies that are available for the Flex System Carrier-Grade chassis are listed in Table 1.
| Rated output | Input voltage range | Power cord connector | FRU numbers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2500 W | -48 to -60 V dc | 2 position power connector | 94Y8265 |
| 2500 W | 200 to 240 V ac | C20 | 94Y8251 or 69Y5890 |
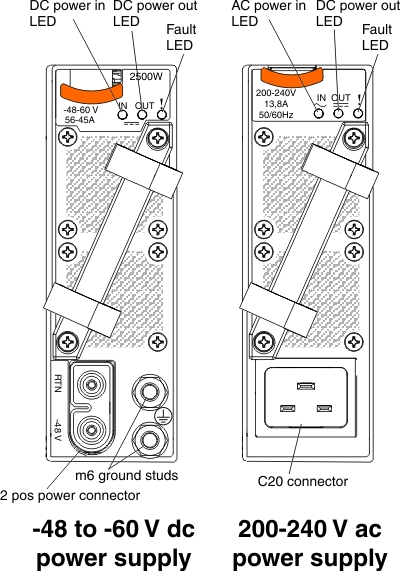
The power supplies get electrical power from either a -48 to -60 V dc power source or a 200 to 240 V ac power source, depending on the type of power supply. Both dc and ac-powered supplies convert the power source into 12 V dc and 3.3 V dc outputs to the system midplane. The power supplies are capable of autoranging within the input voltage range. There is one common power domain for the chassis that distributes dc power to each of the nodes and modules through the system midplane.
Power supply redundancy is achieved when there is one more power supply available than is needed to provide full power to all chassis components. Power source redundancy is achieved by distributing the power cord connections between independent supply circuits. See Connecting the chassis to power for more information.
Each power supply has internal fans and a controller. The power supply controller can be powered by any installed power supply that is providing dc power through the midplane. The power supply does not have to be connected to a power source to communicate with the CMM, as long as dc power is available from the midplane.
Up to six power supplies can be installed. The number of power supplies that you install is dependent on the type of power supply, the chassis power load, and selected chassis power policy.
- 200 - 208 VAC, 3-Phase Delta power distribution units (PDUs): The ac power supplies are designed so that three power supplies will consume the power of and balance the phases of a 30 A, 3-phase PDU; or six power supplies will consume the power of and balance the phases of a 60 A, 3-phase PDU.
- 380 - 450 VAC, 3-Phase Y PDU: The ac power supplies are designed so that three power supplies will nearly consume the power of and balance the phases of a 16A, 3-phase PDU, or six power supplies will nearly consume the power of and balance the phases of a 32 A, 3-phase PDU.
- Single-phase PDUs can be used, however, the building power service may be unbalanced and the PDU power may not be fully utilized.
Power supply controls and indicators
There are three LEDs on each power supply.
| LED | Function |
|---|---|
| DC power in (-48 to -60 V dc supplies only) |  When this LED is lit (green), it indicates that dc power is being supplied to the power supply. |
| AC power in (200 - 240 V ac supplies only) |  When this LED is lit (green), it indicates that ac power is being supplied to the power supply. |
| DC power out |  When this LED is lit (green), it indicates that dc power is being supplied from the power supply to the chassis midplane. |
| Fault | When this LED is lit (yellow), it indicates that there is a fault in the power supply. Note Before unplugging the power cord from the power supply or removing the power supply from the chassis, verify that the capacity of the remaining power supplies are sufficient to meet the minimum power requirements for all components in the chassis. |