Operating modes
Select the operating mode based on your preference.
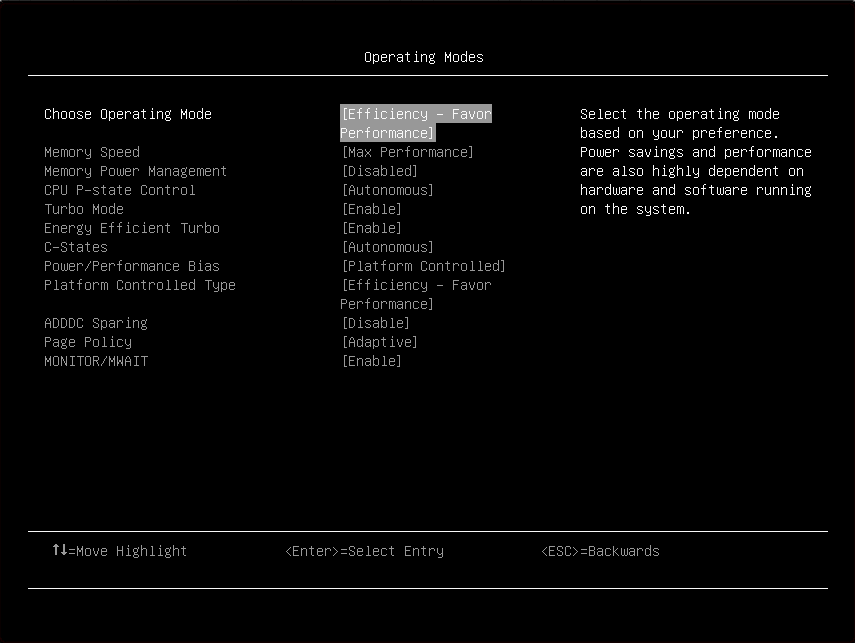
Item | Options | Description |
| Choose Operating Mode |
| Select the operating mode based on your preference. The efficiency of power saving and the system performance are highly dependent on your hardware and software environment.
|
| Memory Speed |
| Select your desired memory speed.
When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings, select . |
| Memory Power Management |
|
When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings, select . |
| CPU P-state Control |
| Select the method to control CPU P-states (performance states).
When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings, select . |
| Turbo Mode |
| Enabling turbo mode can boost the overall CPU performance when all CPU cores are not being fully utilized. A CPU core can run above its rated frequency for a short period of time when it is in turbo mode. When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings, select . |
| Energy Efficient Turbo |
| When energy efficient turbo is enabled, the CPU’s optimal turbo frequency will be tuned dynamically based on CPU utilization. This item is also related to the setting of Power/Performance Bias. When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings:
|
| C-States |
| C-states reduce CPU idle power.
When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings, select . |
| Power/Performance Bias |
| Power/Performance bias determines how aggressively the CPU will be power managed and placed into turbo.
When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings, select . |
| Platform Controlled Type |
|
When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings, select . |
| ADDDC Sparing |
| Enable/Disable ADDDC Sparing. This setting is disabled and grayed out when Page Policy is Adaptive. Enabling ADDDC may cause reduced reliability of memory error correction in virtual lockstep under rare conditions. |
| Page Policy |
|
Note This item will be set to Closed and grayed out when |
| MONITOR/MWAIT |
| MONITOR/MWAIT instructions are used to engage C-states. Some operating systems will re-enable C-states even when they are disabled in setup. To prevent this, you also need to disable this item, and then change the following settings:
|