Processors
This menu displays and provides options to change the processor settings.
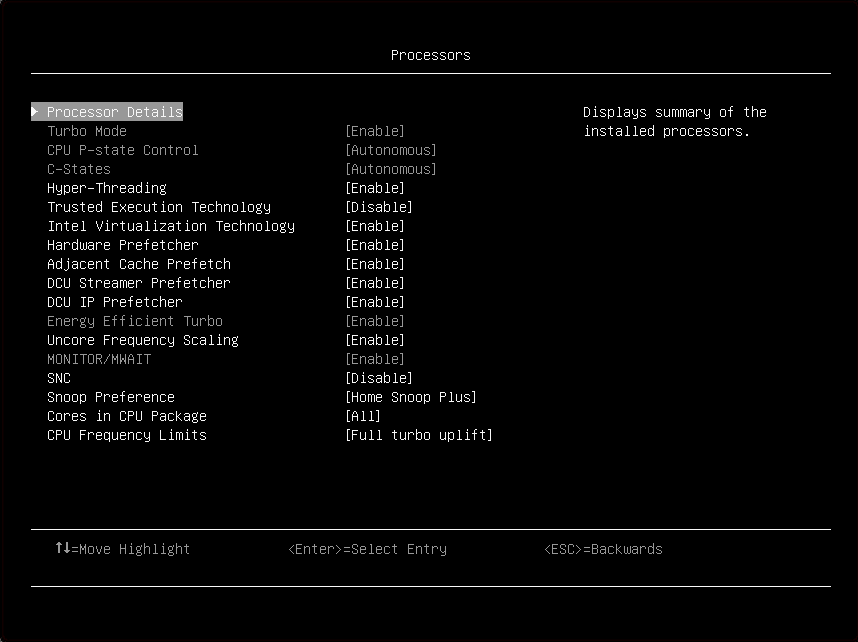
Item | Options | Description |
| Processor details | View the summary of the installed processors. | |
| Turbo Mode Note If the CPU doesn’t support the feature, this item will not be displayed. |
| Enabling turbo mode can boost the overall CPU performance when all CPU cores are not being fully utilized. A CPU core can run above its rated frequency for a short period of time when it is in turbo mode. When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings, select . |
| CPU P-state Control |
| Select a method to control CPU P-states (performance states).
When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings, select . |
| C-States |
| C-states reduce CPU idle power.
When a preset mode is selected, the low-level setting are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings, select . |
| C1 Enhanced Mode Note This item is displayed only when C-state is not Autonomous. |
| Enabling C1E (C1 Enhanced) state saves power by halting CPU cores that are idle. An operating system that supports C1E state must be installed to take advantage of this feature. Setting changes will be taken effect after the next reboot. When a preset mode is selected, the low-level settings are not changeable and will be grayed out. If you would like to change the settings, please follow these steps below:
|
| Hyper-Threading Note If the CPU doesn’t support the feature, this item will not be displayed. |
| Enable Hyper Threading, a software method to enable/disable Logical Processor threads. Note It requires a reboot for the change to take effect. |
| Trusted Execution Technology |
| Enable Intel Trusted Execution Technology (Intel TXT). |
| Intel Virtualization Technology |
| Enable the Virtualization Technology. |
| Hardware Prefetcher |
| Lightly threaded applications and some benchmarks can benefit from having the hardware prefetcher enabled. |
| Adjacent Cache Prefetch |
| Lightly threaded applications and some benchmarks can benefit from having the adjacent cache line prefetch enabled. |
| DCU Streamer Prefetcher |
| Lightly threaded applications and some benchmarks can benefit from having the DCU streamer prefetcher enabled. |
| DCU IP Prefetcher |
| It is recommended that DCU IP prefetcher is set as Enable for most environments. However, some environments may benefit from having it set as Disable, e.g. Java. |
| Energy Efficient Turbo |
|
The power/performance bias setting also influences energy efficient turbo. When a preset mode is selected, the low-level settings are not changeable and will be grayed out. To change the settings:
|
| Uncore Frequency Scaling |
|
|
| MONITOR/MWAIT |
| MONITOR/MWAIT instructions are used to engage C-states. Some operating systems will re-enable C-states even when they are disabled in setup. To prevent this, disable MONNITOR/MWAIT:
|
| SNC |
| SNC (sub NUMA cluster) partitions the cores and the last level cache into clusters with each cluster bound to a set of memory controllers in the system. SNC improves average latency to the last level cache. |
| Snoop Preference |
| Select the appropriate snoop mode based on the workload. However, the snoop mode preference may be changed if the current hardware configuration does not support the desired mode. Also not that SNC has priority over the snoop mode. |
| Cores in CPU Package |
| Select the amount of cores enabled within each CPU Package. The options will be the maximum number of cores that the installed processor supports. For example, if 6 cores are supported, there will be All, 1, 2, 3 4, and 5. |
| CPU Frequency Limits Note This item can be only available when |
| The maximum frequency (turbo, AVX, and non turbo) can be restricted to a frequency that is between the maximum turbo frequency for the CPU installed and 1.2GHz. This can be useful for synchronizing CPU tasks. Note The max frequency for N+1 cores cannot be higher than N cores. If an illegal frequency is entered, it will automatically be limited to a legal value. If the CPU frequency limits are being controlled through application software, leave this item at the default (Full turbo uplift) and change the settings by following these steps below:
|
| CPU Frequency Limits | The maximum frequency (turbo, AVX, and non turbo) can be restricted to a frequency that is between the maximum turbo frequency for the CPU installed and 1.2GHz. This can be useful for synchronizing CPU tasks. Note The max frequency for N+1 cores cannot be higher than N cores. If an illegal frequency is entered, it will automatically be limited to a legal value. If the CPU frequency limits are being controlled through application software, leave this item at the default (Full turbo uplift) and change the settings by following these steps below:
|