Managing servers
Lenovo XClarity Administrator can manage several types of systems, including ThinkAgile, ThinkSystem, Converged, Flex System, NeXtScale, System x®, and ThinkServer® servers.
Before you begin
You can manage a maximum of 300 devices at one time.
After you initiate a device-management operation, wait for the entire management job to complete before initiating another device-management operation.
Flex compute nodes are discovered and managed automatically when you manage the chassis that contains them. You cannot discover and managed Flex compute nodes independent of the chassis.
Review the management considerations before managing a device. For information, see Management considerations.
Certain ports must be available to communicate with devices. Ensure that all required ports are available before you attempt to manage servers. For information about ports, see Port availability.
Ensure that the minimum required firmware is installed on each server that you want to manage using XClarity Administrator. You can find minimum required firmware levels from the XClarity Administrator Support – Compatibility webpage by clicking the Compatibility tab and then clicking the link for the appropriate device types.
- Ensure that CIM over HTTPS is enabled on the device.
Log in to the management web interface for the server using the RECOVERY_ID user account,
Click .
Click the CIM Over HTTPS tab, and ensure that Enable CIM Over HTTPS is selected.
- Some ThinkSystem servers support two XCC IP addresses; however, XClarity Administrator can use only one XCC IP address for management (known as the management IP address). if XClarity Administrator discovers two XCC IP addresses for the same server, only the IP address with the smaller number is list in the discovered devices table.ImportantIf two XCC IP addresses are present on a ThinkSystem server:
Each XCC IP address must be configure on separate subnets.
The IP address that you use to manage the server becomes the management IP address. If there is a connectivity issue with the IP address, XClarity Administrator does not failover to use the second XCC IP address.
For ThinkSystem SR635 and SR655 servers:
Ensure that an operating system is installed, and that the server was booted to the OS, mounted bootable media, or efishell at least once so that XClarity Administrator can collect inventory for those servers.
Ensure that IPMI over LAN is enabled. IPMI over LAN is disabled by default on these servers and must be manually enabled before the servers can be managed. To enable IPMI over LAN using TSM, click . You might need to restart the server to activate the change.
If the device's server certificate is signed by an external certificate authority, ensure that the certificate authority certificate and any intermediate certificates are imported into the XClarity Administrator trust store (see Deploying customized server certificates to managed devices).
- To discover a server that is on a different subnet from XClarity Administrator, ensure that one of the following conditions are met:
Ensure that you enable multicast SLP forwarding on the top-of-rack switches, as well as the routers in your environment. See the documentation that was provided with your specific switch or router to determine whether multicast SLP forwarding is enabled and to find procedures to enable it if it is disabled.
If SLP is disabled on the endpoint or on the network, you can use DNS discovery method instead by manually adding a service record (SRV record) to your domain name server (DNS), for XClarity Administrator for example
_lxca._tcp.labs.lenovo.com service = 0 0 443 fvt-xhmc3.labs.lenovo.com.Then, enable DNS discovery on the baseboard management console from the management web interface, by clicking , clicking the DNS tab, and selecting Use DNS to discover Lenovo XClarity Administrator.
NoteThe management controller must be running a firmware level dated May 2017 or later to support automatic discovery using DNS.
If there are multiple XClarity Administrator instances in your environment, the server is discovered only by the instance that is the first to respond to the discovery request. The server is not discovered by all instances.
- To discover and manage ThinkServer servers, ensure that the following requirements are met. For more information, see Cannot discover a device and Cannot manage a device.
The hostname of the server must be configured using a valid hostname or IP address if you want XClarity Administrator to discover the servers automatically.
The network configuration must allow SLP traffic between XClarity Administrator and the server.
Unicast SLP is required.
If you want XClarity Administrator to automatically discover ThinkServer servers, multicast SLP is required. In addition, SLP must be enabled on the ThinkServer System Manager (TSM).
If ThinkServer servers are on a different network than XClarity Administrator, ensure that the network is configured to allow inbound UDP through port 162 so that XClarity Administrator can receive events for those devices.
For ThinkAgile, ThinkSystem, Converged, Flex System. NeXtScale, and System x servers, if you remove, replace, or configure any adapters in the server, restart the server at least once to update the new adapter information in the baseboard management controller and XClarity Administrator reports (Powering on and off a server).
When performing management actions on a server, ensure that the server is either powered off or powered on to the BIOS/UEFI Setup or to a running operating system. (You can boot to BIOS/UEFI Setup from the Servers page in XClarity Administrator by clicking .) If server is powered on without an operating system, the management controller continuously resets the server in an attempt to find an operating system.
- Ensure that all UEFI_Ethernet_* and UEFI_Slot_* settings are enabled in the server UEFI Settings. To verify the settings, restart the server and when the prompt <F1> Setup is displayed, press F1 to start the Setup utility. Navigate to , and then locate the Enable / Disable UEFI Option ROM(s) section to verify that the settings are enabled.NoteIf supported, you can also use the Remote Console feature in the baseboard management interface to review and modify the settings remotely.
System x3950 X6 servers must be managed as two 4U enclosures, each with its own baseboard management controller.
About this task
XClarity Administrator can automatically discover rack and tower servers in your environment by probing for manageable devices that are on the same IP subnet as XClarity Administrator. To discover rack and tower servers that are in other subnets, specify an IP address or range of IP addresses, or import information from a spreadsheet.
After the servers are managed by XClarity Administrator, Lenovo XClarity Administrator polls each managed server periodically to collect information, such as inventory, vital product data, and status. You can view and monitor each managed server and perform management actions (such as configuring system settings, deploying operating-system images, and powering on and off).
When local authentication is used for rack servers, Lenovo chassis, and Lenovo rack switches, XClarity Administrator uses a stored credential to authenticate to the device. The stored credential can be an active user account on the device or a user account in an Active Directory server.
You must create a stored credential in XClarity Administrator that matches an active user account on the device or a user account in an Active Directory server before managing the device using local authentication (see Managing stored credentials).
Note- When local authentication is enabled for a device, you cannot edit stored credentials for that device using XClarity Administrator.
- RackSwitch devices support only stored credentials for authentication. XClarity Administrator user credentials are not supported.
Using managed authentication allows you to manage and monitor multiple devices using credentials in the XClarity Administrator authentication server instead of local credentials. When managed authentication is used for a device (other than ThinkServer servers, System x M4 servers, and switches), XClarity Administrator configures the device and its installed components to use the XClarity Administrator authentication server for centralized management.
- When managed authentication is enabled, you can manage devices using either manually-entered or stored credentials (see Managing user accounts and Managing stored credentials).
The stored credential is used only until XClarity Administrator configures the LDAP settings on the device. After that, any change to the stored credential has no impact the management or monitoring of that device.
- If a local or external LDAP server is used as the XClarity Administrator authentication server, user accounts that are defined in the authentication server are used to log in to XClarity Administrator, CMMs and baseboard management controllers in the XClarity Administrator domain. Local CMM and management controller user accounts are disabled.NoteFor Think Edge SE100, SE450, SE455, SE350 V2, and SE360 V2 servers, the default local user account remains enabled and all other local accounts are disabled.
- If an SAML 2.0 identity provider is used as the XClarity Administrator authentication server, SAML accounts are not accessible to managed devices. However, when using an SAML identity provider and an LDAP server together, if the identity provider uses accounts that exist in the LDAP server, LDAP user accounts can be used to log into the managed devices while the more advanced authentication methods that are provided by SAML 2.0 (such as multifactor authentication and single sign-on) can be used to log into XClarity Administrator.
- Single sign-on allows a user that is already logged in to XClarity Administrator to automatically log in to the baseboard management control. Single sign-on is enabled by default when a ThinkSystem or ThinkAgile server is brought into management by XClarity Administrator (unless the server is managed with CyberArk passwords). You can configure the global setting to enable or disable single sign-on for all managed ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile servers. Enabling single sign-on for a specific ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile server overrides the global setting for all ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile servers (see Managing servers).NoteSingle sign-on is disabled automatically when using the CyberArk identity-management system for authentication.
- When managed authentication is enabled for ThinkSystem SR635 and SR655 servers:
- Baseboard management-controller firmware supports up to five LDAP user roles. XClarity Administrator adds these LDAP user roles to the servers during management: lxc-supervisor, lxc-sysmgr, lxc-admin, lxc-fw-admin, and lxc-os-admin.
Users must be assigned to at least one of the specified LDAP user roles to communicate with ThinkSystem SR635 and SR655 servers.
- Management-controller firmware does not support LDAP users with the same username as local user of the sever.
- Baseboard management-controller firmware supports up to five LDAP user roles. XClarity Administrator adds these LDAP user roles to the servers during management: lxc-supervisor, lxc-sysmgr, lxc-admin, lxc-fw-admin, and lxc-os-admin.
For ThinkServer and System x M4 servers, the XClarity Administrator authentication server is not used. Instead, an IPMI account is created on the device with the prefix
LXCA_
followed by a random string. (The existing local IPMI user accounts are not disabled.) When you unmanage a ThinkServer server, theLXCA_
user account is disabled, and the prefixLXCA_
is replaced with the prefixDISABLED_
. To determine whether a ThinkServer server is managed by another instance, XClarity Administrator checks for IPMI accounts with the prefixLXCA_
. If you choose to force management of a managed ThinkServer server, all the IPMI accounts on the device with theLXCA_
prefix are disabled and renamed. Consider manually clearing IPMI accounts that are no longer used.If you use manually-entered credentials, XClarity Administrator automatically creates a stored credential and uses that stored credential to manage the device.
NoteWhen managed authentication is enabled for a device, you cannot edit stored credentials for that device usingXClarity Administrator. - Each time you manage a device using manually-entered credentials, a new stored credential is created for that device, even if another stored credential was created for that device during a previous management process.
- When you unmanage a device, XClarity Administrator does not delete stored credentials there were automatically created for that device during the management process.
- When managed authentication is enabled, you can manage devices using either manually-entered or stored credentials (see Managing user accounts and Managing stored credentials).
A device can be managed by only one XClarity Administrator instance at a time. Management by multiple XClarity Administrator instances is not supported. If a device is managed by one XClarity Administrator, and you want to manage it with another XClarity Administrator, you must first unmanage the device on the initial XClarity Administrator, and then manage it with the new XClarity Administrator. If an error occurs during the unmanagement process, you can select the Force management option during management on the new XClarity Administrator.
- Logs in to the server using the provided credentials.
- Collects inventory for each server.NoteSome inventory data is collected after the management process completes. You cannot perform certain tasks on a managed server (such as deploying a server pattern) until all inventory data is collected for that server and the server is no longer in the Pending state.
- Configures settings for the NTP server so all managed devices use the same NTP server configuration that is configured on XClarity Administrator.
- (System x and NeXtScale severs only) Assigns the last-edited firmware-compliance policy to the server.
- (Lenovo System x and NeXtScale severs only) Optionally configures the devices firewall rules so that incoming requests from only XClarity Administrator are accepted.
- (System x and NeXtScale severs only) Exchanges security certificates with the management controller, copying the CIM server certificate and the LDAP client certificate from the management controller into the XClarity Administrator trust store and sending the XClarity Administrator CA security certificate and LDAP trust certificates to the management controller. The management controller loads the certificates into the management-controller trust store so that the management controller can trust connections to the LDAP and CIM servers on the XClarity Administrator.NoteIf the CIM server certificate or LDAP client certificate does not exist, it is created during the management process.
Configures managed authentication, if applicable. For more information about managed authentication, see Managing the authentication server.
Creates the recovery user account (RECOVERY_ID), when applicable. For more information about the RECOVERY_ID account, see Managing the authentication server.
Procedure
To manage your rack and tower servers using XClarity Administrator, complete one of the following procedures.
Discover and manage a large number of tower and rack servers and other devices using a bulk-import file (see Managing devices).
Discover and manage rack and tower servers that are on the same IP subnet as XClarity Administrator.
From the XClarity Administrator menu bar, click . The Discover and Manage New Devices page is displayed.
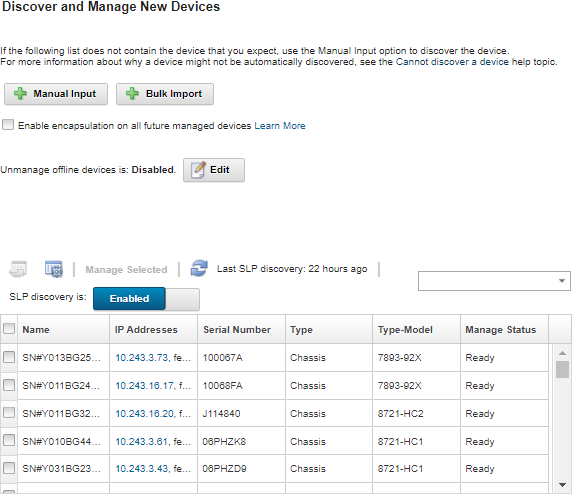
You can sort the table columns to make it easier to find the servers that you want to manage. In addition, you can enter text (such as a name or IP address) in the Filter field to further filter the servers that are displayed. You can change the columns that are displayed and the default sort order by clicking the Customize Columns icon (
 ).
).Click the Refresh icon (
 ) to discover all manageable devices in the XClarity Administrator domain. Discovery might take several minutes.
) to discover all manageable devices in the XClarity Administrator domain. Discovery might take several minutes.Click the Enable encapsulation on all future managed devices checkbox to change the firewall rules on all devices during the management process so that incoming requests are accepted from only XClarity Administrator.
Encapsulation can be enabled or disabled on specific devices after they are managed.
NoteWhen the management network interface is configured to use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and when encapsulation enabled, managing a rack server can take a long time.AttentionIf encapsulation is enabled andXClarity Administrator becomes unavailable before a device is unmanaged, necessary steps must be taken to disable encapsulation to establish communication with the device. For recovery procedures, see lenovoMgrAlert.mib file and Recovering management with a CMM after a management server failure. Select one or more servers that you want to manage.
Click Manage Selected. The Manage dialog is displayed.
Choose to use XClarity Administrator managed authentication or local authentication for this device. Managed authentication is selected by default. To use local authentication, clear Managed Authentication.
Choose the type of credentials to use to authenticate to the device and specify the appropriate credentials:
Use manually entered credentials
Specify the user ID and password for authenticating to the server.
(Optional) Set a new password for the specified user name if the password is currently expired on the device.
NoteFor ThinkSystem V4 servers, external LDAP usernames are case sensitive.
To use manually entered credentials, you must select XClarity Administrator managed authentication.
Use stored credentials
Select the stored credential to use for this managed device. You can create a new stored credential by clicking Create New.
Use identity-management system
Select the identity management system that you want to use for this managed device. Then, fill in the remaining fields, including the IP address or host name of the managed server, user name, and optionally application ID, safe and folder.
If you specify the application ID, you must also specify the safe and folder, if applicable.
If you do not specify the application ID, XClarity Administrator uses the paths that were defined when you setup CyberArk to identify the onboarded accounts in CyberArk (see Setting up a CyberArk identity-management systemSetting up a CyberArk identity-management system in the XClarity Administrator online documentation).
NoteOnly ThinkSystem or ThinkAgile servers are supported. The identity management system must be configured inXClarity Administrator, and the Lenovo XClarity Controller for the managed ThinkSystem or ThinkAgile servers must be integrated with CyberArk (see Setting up a CyberArk identity-management systemSetting up a CyberArk identity-management system in the XClarity Administrator online documentation).
TipIt is recommended to use a supervisor or administrator account to manage the device. If an account with lower level authority is used, management might fail, or management might succeed but otherXClarity Administrator operations on the device might fail (particularly if the device is managed without managed authentication). For more information about normal and stored credentials, see Managing user accounts and Managing stored credentials.
Specify the recovery password if managed authentication is selected.
When a password is specified, the recovery account (RECOVERY_ID) is created on the server, and all local user accounts are disabled. If there is a problem with XClarity Administrator, and it stops working for some reason, you cannot log in to the management controller using normal user accounts. However, you can log in using the recovery account.
NoteThe recovery password is optional if you choose to use managed authentication and is not allowed if you if you choose to use local authentication.
You can choose to use a local recovery account or stored recovery credentials. In either case, the user name is always RECOVERY_ID.
Ensure that the password follows the security and password policies for the device. Security and password policies might vary.
Ensure that you record the recovery password for future use.
The recovery account is not supported for ThinkServer and System x M4 servers.
For more information about the recovery ID, see Managing the authentication server.
Click Change to change the role groups that are to be assigned to the devices.
NoteYou can select from a list of role groups that are assigned to the current user.
If you do not change the role groups, the default role groups are used. For more information about the default role groups, see Changing the default permissions.
Click Manage.
A dialog is displayed that shows the progress of this management process. To ensure that the process completes successfully, monitor the progress.
When the process is complete, click OK.
The device is now managed by XClarity Administrator, which automatically polls the managed device on a regular schedule to collect updated information, such as inventory.
If management was not successful due to one of the following error conditions, repeat this procedure using the Force management option.
If the managing XClarity Administrator failed and cannot be recovered.
NoteIf the replacementXClarity Administrator instance uses the same IP address as the failed XClarity Administrator, you can manage the device again using the RECOVERY_ID account and password (if applicable) and the Force management option. If the managing XClarity Administrator was taken down before the devices were unmanaged.
If the devices were not unmanaged successfully.
AttentionDevices can be managed by only oneXClarity Administrator instance at a time. Management by multiple XClarity Administrator instances is not supported. If a device is managed by one XClarity Administrator, and you want to manage it with another XClarity Administrator, you must first unmanage the device from the original XClarity Administrator, and then manage it with the new XClarity Administrator.
Discover and manage rack and tower servers that are not on the same IP subnet as XClarity Administrator by manually specifying IP addresses.
From the XClarity Administrator menu bar, click . The Discover and Manage page is displayed.
Click the Enable encapsulation on all future managed devices checkbox to change the firewall rules on all devices during the management process so that incoming requests are accepted from only XClarity Administrator.
Encapsulation can be enabled or disabled on specific devices after they are managed.
NoteWhen the management network interface is configured to use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and when encapsulation enabled, managing a rack server can take a long time.AttentionIf encapsulation is enabled andXClarity Administrator becomes unavailable before a device is unmanaged, necessary steps must be taken to disable encapsulation to establish communication with the device. For recovery procedures, see lenovoMgrAlert.mib file and Recovering management with a CMM after a management server failure. Select Manual Input.
Specify the network addresses of the servers that you want to manage:
- Click Single System, and enter a single IP address domain name, or fully-qualified domain name (FQDN).Network AccessTo specify an FQDN, ensure that a valid domain name is specified on
page (see Configuring network access). - Click Multiple Systems, and enter a range of IP addresses. To add another range, click the Add icon (
 ). To remove a range, click the Remove icon (
). To remove a range, click the Remove icon ( ).
).
- Click Single System, and enter a single IP address domain name, or fully-qualified domain name (FQDN).
Click OK. The Manage dialog is displayed
Choose to use XClarity Administrator managed authentication or local authentication for this device. Managed authentication is selected by default. To use local authentication, clear Managed Authentication.
Choose the type of credentials to use to authenticate to the device and specify the appropriate credentials:
Use manually entered credentials
Specify the user ID and password for authenticating to the server.
(Optional) Set a new password for the specified user name if the password is currently expired on the device.
NoteFor ThinkSystem V4 servers, external LDAP usernames are case sensitive.
To use manually entered credentials, you must select XClarity Administrator managed authentication.
Use stored credentials
Select the stored credential to use for this managed device. You can create a new stored credential by clicking Create New.
Use identity-management system
Select the identity management system that you want to use for this managed device. Then, fill in the remaining fields, including the IP address or host name of the managed server, user name, and optionally application ID, safe and folder.
If you specify the application ID, you must also specify the safe and folder, if applicable.
If you do not specify the application ID, XClarity Administrator uses the paths that were defined when you setup CyberArk to identify the onboarded accounts in CyberArk (see Setting up a CyberArk identity-management systemSetting up a CyberArk identity-management system in the XClarity Administrator online documentation).
NoteOnly ThinkSystem or ThinkAgile servers are supported. The identity management system must be configured inXClarity Administrator, and the Lenovo XClarity Controller for the managed ThinkSystem or ThinkAgile servers must be integrated with CyberArk (see Setting up a CyberArk identity-management systemSetting up a CyberArk identity-management system in the XClarity Administrator online documentation).
TipIt is recommended to use a supervisor or administrator account to manage the device. If an account with lower level authority is used, management might fail, or management might succeed but otherXClarity Administrator operations on the device might fail (particularly if the device is managed without managed authentication). For more information about normal and stored credentials, see Managing user accounts and Managing stored credentials.
Specify the recovery password if managed authentication is selected.
When a password is specified, the recovery account (RECOVERY_ID) is created on the server, and all local user accounts are disabled. If there is a problem with XClarity Administrator, and it stops working for some reason, you cannot log in to the management controller using normal user accounts. However, you can log in using the recovery account.
NoteThe recovery password is optional if you choose to use managed authentication and is not allowed if you if you choose to use local authentication.
You can choose to use a local recovery account or stored recovery credentials. In either case, the user name is always RECOVERY_ID.
Ensure that the password follows the security and password policies for the device. Security and password policies might vary.
Ensure that you record the recovery password for future use.
The recovery account is not supported for ThinkServer and System x M4 servers.
For more information about the recovery ID, see Managing the authentication server.
Click Change to change the role groups that are to be assigned to the devices.
NoteYou can select from a list of role groups that are assigned to the current user.
If you do not change the role groups, the default role groups are used. For more information about the default role groups, see Changing the default permissions.
Click Manage.
A dialog is displayed that shows the progress of this management process. To ensure that the process completes successfully, monitor the progress.
When the process is complete, click OK.
The device is now managed by XClarity Administrator, which automatically polls the managed device on a regular schedule to collect updated information, such as inventory.
If management was not successful due to one of the following error conditions, repeat this procedure using the Force management option.
If the managing XClarity Administrator failed and cannot be recovered.
NoteIf the replacementXClarity Administrator instance uses the same IP address as the failed XClarity Administrator, you can manage the device again using the RECOVERY_ID account and password (if applicable) and the Force management option. If the managing XClarity Administrator was taken down before the devices were unmanaged.
If the devices were not unmanaged successfully.
AttentionDevices can be managed by only oneXClarity Administrator instance at a time. Management by multiple XClarity Administrator instances is not supported. If a device is managed by one XClarity Administrator, and you want to manage it with another XClarity Administrator, you must first unmanage the device from the original XClarity Administrator, and then manage it with the new XClarity Administrator.
After you finish
- Discover and manage additional devices.
- Configure the system information, local storage, I/O adapters, boot topics, and firmware settings by creating and deploying server patterns (see Configuring servers using configuration patterns).
- Deploy operating-system images to servers that do not already have an operating system installed (see Installing operating systems on bare-metal servers).
- Update firmware on devices that are not in compliance with current policies (see Updating firmware on managed devices).
- Add the devices to the appropriate rack to reflect the physical environment (see Managing racks).
- Monitor hardware status and details (see Viewing the status of a managed server).
- Monitor events and alerts (see Working with events and Working with alerts).
- Clear the SEL log for a server by clicking from the XClarity Administrator menu bar, selecting the server, and then clicking .
This action is supported for only ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile servers.
Resolve stored credentials that have become expired or invalid (see Managing stored credentials).
- Enable or disable single sign-on for all managed ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile servers by clicking from the XClarity Administrator menu bar, clicking Active Sessions, and then enabling or disabling Single Sign-On.
- Disable or enable single sign-on for managed ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile servers.
For all managed ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile servers (globally), click from the XClarity Administrator menu bar, click Active Sessions, and then enable or disable Single Sign-On
For a specific ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile server, click from the XClarity Administrator menu bar, and then click or .
NoteSingle sign-on allows a user that is already logged in to XClarity Administrator to automatically log in to the baseboard management control. Single sign-on is enabled by default when a ThinkSystem or ThinkAgile server is brought into management by XClarity Administrator (unless the server is managed with CyberArk passwords). You can configure the global setting to enable or disable single sign-on for all managed ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile servers. Enabling single sign-on for a specific ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile server overrides the global setting for all ThinkSystem and ThinkAgile servers.