Independent memory mode
In independent memory mode, memory channels can be populated with DIMMs in any order and you can populate all channels for each processor in any order with no matching requirements. Independent memory mode provides the highest level of memory performance, but lacks failover protection. The DIMM installation order for independent memory mode varies based on the number of processors and memory modules installed in the compute node.
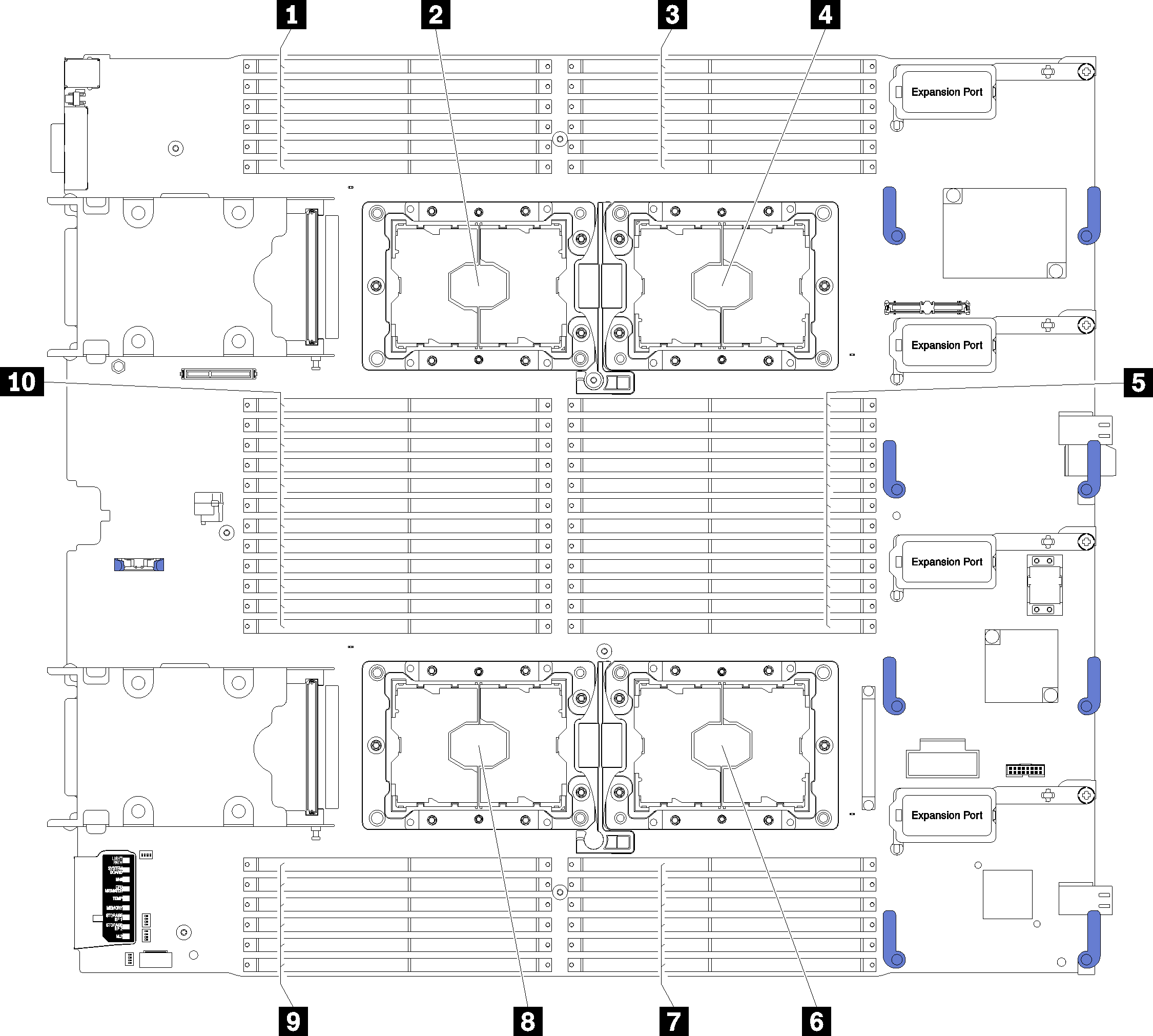
| 1 DIMM 25 – 30 | 6 Processor socket 2 |
| 2 Processor socket 3 | 7 DIMM 19 – 24 |
| 3 DIMM 1 – 6 | 8 Processor socket 4 |
| 4 Processor socket 1 | 9 DIMM 43 – 48 |
| 5 DIMM 7 – 18 | 10 DIMM 31 – 42 |
| Memory controllers | Controller 0 | Controller 1 | |||||||||||
| Channels | Channel 2 | Channel 1 | Channel 0 | Channel 0 | Channel 1 | Channel 2 | |||||||
| Slots | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| DIMM numbers (processor 1) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| DIMM numbers (processor 2) | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | |
| Memory controllers | Controller 1 | Controller 0 | |||||||||||
| Channels | Channel 2 | Channel 1 | Channel 0 | Channel 0 | Channel 1 | Channel 2 | |||||||
| Slots | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| DIMM numbers (processor 3) | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | |
| DIMM numbers (processor 4) | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | |
Individual memory channels can run at different DIMM timings, but all channels must run at the same interface frequency.
Populate memory channel 0 first.
Memory channel 1 is empty or identically populated as memory channel 0.
Memory channel 2 is empty or identically populated as memory channel 1.
In each memory channel, populate slot 0 first.
If a memory channel has two DIMMs, populate the DIMM with a higher number of ranks in slot 0. If the ranks are the same, populate the one with higher capacity in slot 0.
When a processor populates three identical DIMMs (same part number), populate all on memory controller 0; otherwise, follow the general population rule.
When a processor populates ten identical DIMMs (same part number), populate;five DIMMs on memory controller 0 and five DIMMs on memory controller 1; otherwise, follow the general population rule.